How AI, RPA and Cloud
impact Financial Services
- AI/ML, Cloud, Data Warehousing, Finance, RPA

In the first part of our Digital Finance Transformation blog post series, we shed light on Blockchain as a leading technology. ‘Part 2’ focuses on even more innovations; AI (Artificial Intelligence), RPA (Robotic Process Automation), Cloud Architecture, and Data warehousing are inventions that drive digitalization, and we will illustrate how they can be leveraged.
Artificial Intelligence
In general, AI can be described as the capacity of computers to execute functions that would normally require human intellect, such as visual perception, natural language comprehension, and decision-making. Finance companies usually adopt this technology within their operations to automate a large part of daily routines and minimize the room for errors.
JPMorgan Chase, for example, announced the debut of COIN (short for “contract intelligence”), an AI-powered digital assistant that will be used to automate the process of analyzing commercial loan agreements. The program is able to read and comprehend legal papers faster and more precisely than paralegals and lawyers. COIN filters roughly 12,000 contracts per year, saving 360,000 hours of labor, according to company reports.
Further, organizations also deploy AI-powered solutions to provide their customers with a better experience and user-friendliness, like MX, which uses this emerging technology to analyze customer data and provide recommendations on how to improve the customer’s financial health.
If you are particularly interested in this subject, to further your research we also recommend reading another blog: AI use cases in Finance.
RPA
According to a recent Gartner study, 80% of Finance leaders surveyed have already adopted or are planning to expand RPA technologies in their firms. RPA is being used by banks and other organizations for a variety of objectives, including automating customer onboarding, fraud detection, and loan processing.
Loan Processing
– The first one is the pre-approval of loans, where the collection and verification of customer data can be automated with RPA. This data can then be fed into a decision engine that will provide a decision on whether or not to approve the loan.
– The second use case is post-loan approval, where RPA serves to automate the process of disbursing the loan amount to the borrower’s account. This process usually involves manual intervention, which is time-consuming and can lead to errors. By automating this process with RPA, institutions can reduce processing time and improve accuracy

Fraud Detection
For example, a bank may set up a rule that will flag all transactions above $1000 that are made within 24 hours of opening an account. By automating this process, banks can reduce the time taken to identify and flag fraudulent transactions.
Customer Onboarding
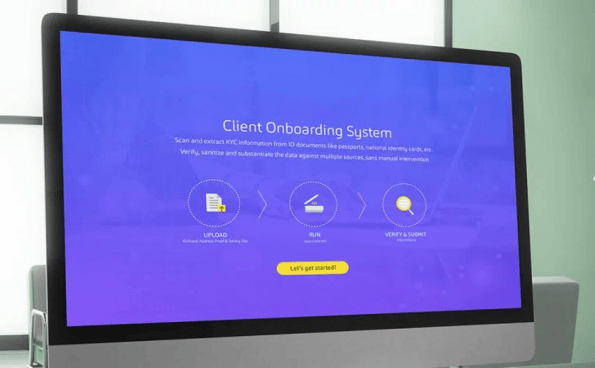
In collaboration with a global asset management company, Elastech developed a similar solution in the form of a cloud-based, due diligence and transaction monitoring system that enables affluent individuals to move their assets quickly and easily, while adhering to financial compliance requirements. This new application allowed the client to reduce a 30-40 day asset migration process down to a few hours. Due to the help of automated due diligence, customer acquisition costs were also decreased by up to 80%. Visit the dedicated case study to learn more about it.
Cloud Adoption
In simple terms, cloud computing is the delivery of computing services – including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. Today, there is an increasing list of possible solutions and vendors for organizations to choose from.
AWS (Amazon Web Services), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are among the most popular platforms with major suppliers. In addition, there is also the option for companies to designate whether to choose a:
– Private cloud (infrastructure used exclusively by the company within it is set up)
– Public cloud (architecture that is used by multiple companies or users)
– Hybrid cloud (a mix of two different cloud types with one being public while the other is private)
– Multi-cloud solution (a company uses multiple cloud providers)
A great number of companies have already begun a migrate-to-cloud strategy to benefit from the power and scale that cloud infrastructure provides, but what are financial institutions specifically doing to take advantage?
Reporting and Analytics
Organizations can also exploit the platform to create dashboards that provide real-time visibility into their business. This helps to identify trends or issues so that they can be addressed quickly.
A good example of a company that is deploying a cloud-based reporting and analytics platform is Barclays, which created a dashboard that provides visibility into customer behavior allowing the bank to identify trends and offer products and services that are better suited to customers’ needs.
Launching New Products
Financial institutions are provided flexibility and scalability when choosing to host their applications in the cloud, rather than on-premises. It is easier for them to quickly roll out new services and features to their customers. This equips them to swiftly adapt and meet customer demands, and respond to changes in the financial market or regulatory environment.
Together with Equifax, we worked on a broad initiative to capitalize on these benefits. Equifax provides more than 3,000 financial services applications to customers across the U.S., requiring them to be compliant with the regulations of each of the 50 states. At first, we migrated their applications from the data center to Google Cloud Platform (“GCP”). Based on that, we were able to compile a cloud-based CI/CD pipeline toolset to automate the pipeline. Leveraging the powerful cloud environment along with our policy-as-code approach, we ensured that the requirements of every state are met automatically. Resulting in the ability to maintain and update applications without the prior dependence on an entire engineering department for support.
If this case study has caught your attention, we invite you to learn more on our website.

Data Warehouse
Next to the deployment of Cloud architecture, RPA as well as Artificial Intelligence, Data Warehousing is the last trend within the Digital Finance Transformation to discuss. With the creation of this approach, large amounts of financial data can be stored and analyzed. This can serve to track trends over time or to identify relationships between different data sets.
By deploying a cloud-based data warehouse, finance organizations reduce the time and cost associated with managing physical data centers, and allow them to avoid capital expenditures (CAPEX) for hardware, software, and labor resources.
One of the first financial institutions to implement a cloud-based data warehouse was Goldman Sachs. Following a hybrid cloud approach, the company built its own private cloud, in addition to its Amazon Web Services (AWS) public cloud. Goldman Sachs was able to reduce the time to process inquiries from minutes to seconds while also reducing its costs by 50%. Other banks such as JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America have followed and are now taking advantage of modern Data Warehousing solutions.

As we have discussed Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence as well as RPA, Cloud Adoption, and Data warehousing, there is another particularly interesting field we want to introduce: Augmented / Virtual Reality. This emerging technology will particularly influence the way financial institutions interact, not only with their customers but also with their employees in the future. ‘Part 3’ of this blog series will be dedicated primarily to AR/VR and its applications within financial institutions. We will also share our thoughts on future deployments that could easily evolve from innovative ideas to industry norms ahead. Watch this space for more interesting content and emerging solutions.
Book your free appointment with a Technical Expert
How companies need to play in order to win the war for telent
